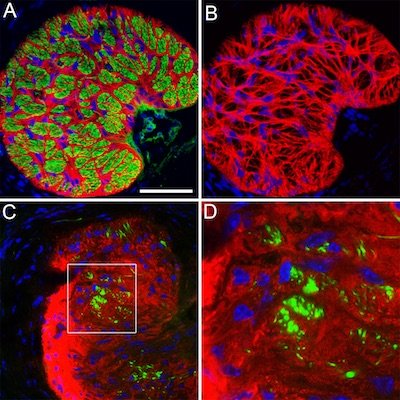
Cross section through a normal glial lamina with GFAP+ astrocytes in red, axons (neurofilament) in green, and cell nuclei counterstained in blue. Credit: Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science February 2013, Vol.54, 909-917. Copyright 2013 Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology
Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness throughout the world. It is often called the sneak thief of vision because it can develop without obvious symptoms. Current therapies aiming to reduce the rate of vision loss only work in some patients and may lead to vision-threatening complications. The search for novel therapies and prevention of Glaucoma relies on better understanding disease mechanisms. This is what the Lasker/IRRF Initiative for Innovation in Vision Science set out to accomplish when it launched its first study in 2009. A recent article titled “The Vision Thief” published in the Atlas of Science describes some of the exciting progress of this initiative.
